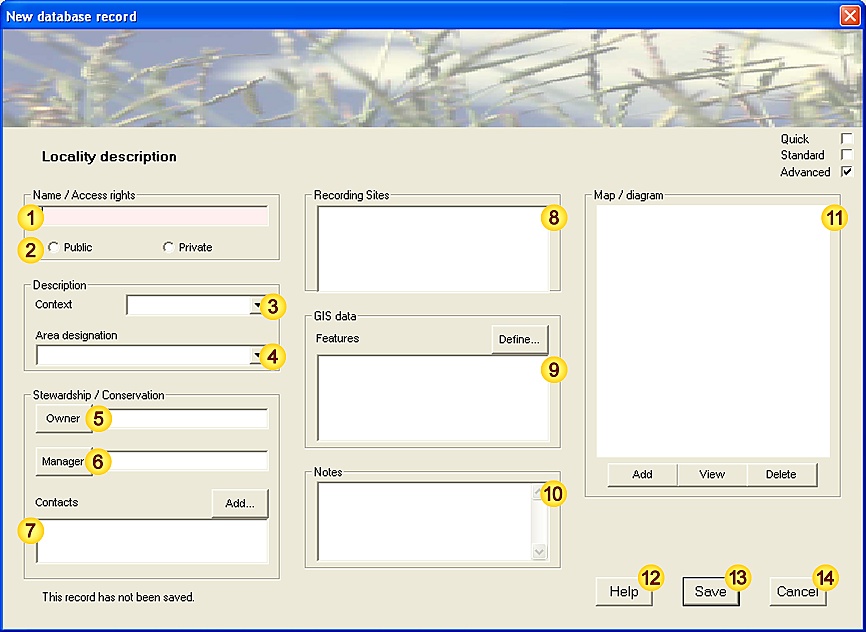
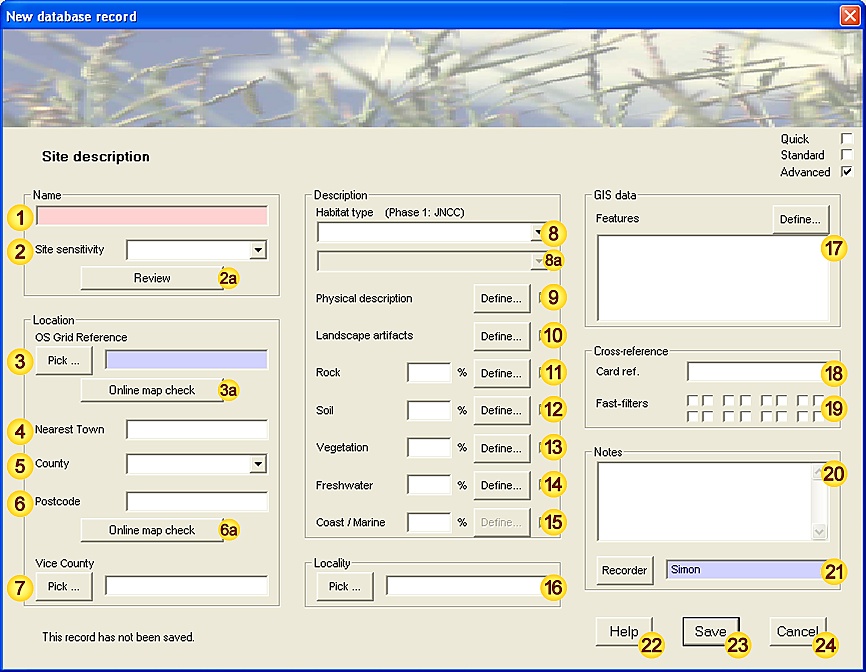
1. Data-entry dialog (level-of-detail: advanced):
2. Input fields - data description:
| Field | Notes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
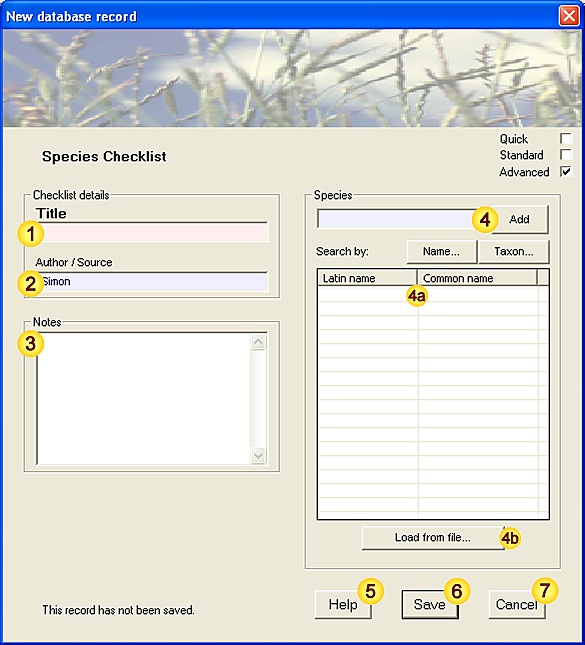
| Species | Species name (common or latin name). See Species-data tool for a more detailed description of functionality. |
|||||||||||||
| Species entry(ies) | These fields (Latin name / Common name) are auto-generated from field and may not be modified. [Mandatory - this field must be completed.] [Fixed-length field - 80 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Abundance | The total number of individuals seen (males+females+immature). This field will also recognise DAFOR abundance values. When recording multiple species (ie. from a checklist), fields without abundance data will be ignored. [Mandatory - this field must be completed.] [When species are added individually, this field is preset to 1 for each species.] [When species are added by checklist, this field is left blank allowing you to choose which species to record.] |
|||||||||||||
| Status | Species status, material evidence supporting the observation or verified absence. [Values: Alive, Dead, Tracks, Call, Nest/den (breeding), Nest/den/roost (non-breeding), Droppings, Pellets, Exuviae, Pollen, Web/case, Other, Absent.] |
|||||||||||||
| Notes | Can be used to provide additional species-related information (eg. sex(es), developmental stages, error estimates etc.). [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Record Sensitivity | A measure of the relative importance of this Observation, both in terms of national rarity status and personal considerations. This information allows you to manage sensitive records more easily, for example when exporting datasets.
[Fixed-length field - 28 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
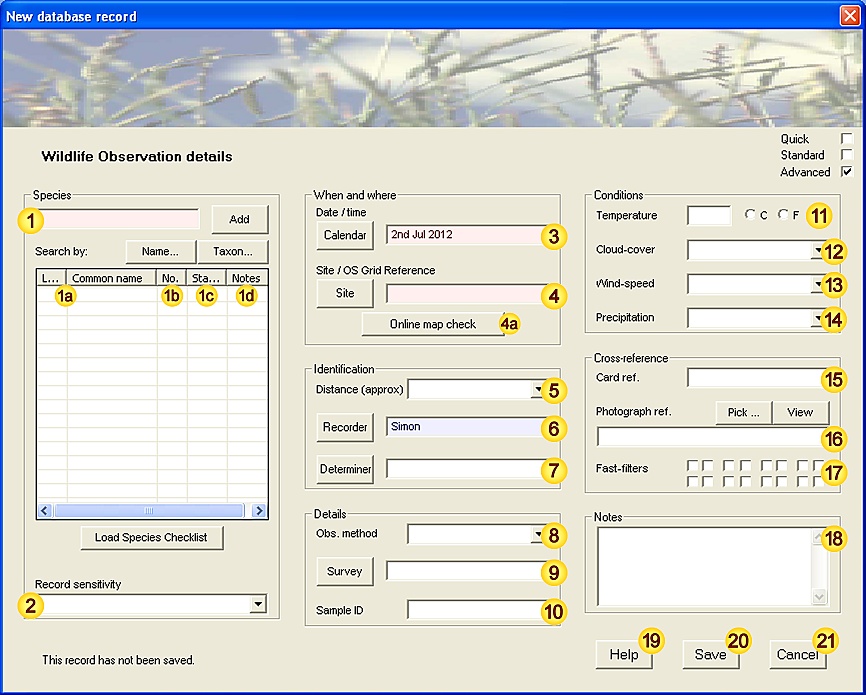
| Date / time | Date (and optionally time) of this Observation (see Note 3.1 for acceptable formats). The Calendar button allows you to select the date using the Calendar tool. [Mandatory - this field must be completed.] [This field is preset with the current date.] [Fixed-length field - 1 date/time value.] |
|||||||||||||
| Location | The place where this Observation was made - may be either a Site name or a valid OS Grid reference. [Mandatory - this field must be completed.] [Fixed-length field - 80 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Online check | Display the given location (Site or OS Grid reference), using an online map resource. This tool requires an open internet connection. |
|||||||||||||
| Distance | Estimated distance between the recorder and species recorded. This information can provide a useful measure of confidence in unusual or confusing species. [Values: <0.2m, 0.2-0.5m, 0.5-2m, 2-5m, 5-20m, 20-50m, 50-200m, 200-500m, 0.5-2km, 2-5km.] |
|||||||||||||
| Recorder | The person making the Observation. [Advisory - this field should be completed wherever possible.] [This field is preset with the name of the current user.] [Fixed-length field - 32 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Determiner | The person authoritatively confirming the Observation - generally an expert in the relevant field. (A determiner is required for positively identifying commonly confused, unusual or rare species - in most other cases this field will be empty). [Fixed-length field - 32 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Observation Method | The means by which this species was encountered - incidental sighting or by various surveying techniques [Values: Timed count, Timed max., Net sample, Species survey, Transect count, Area count, Quadrat, Volume count, Container sample, Baited Trap, Light Trap, Pitfall trap, Bait, Assembling, Pheromone lure, Other.] [Fixed-length field - 32 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
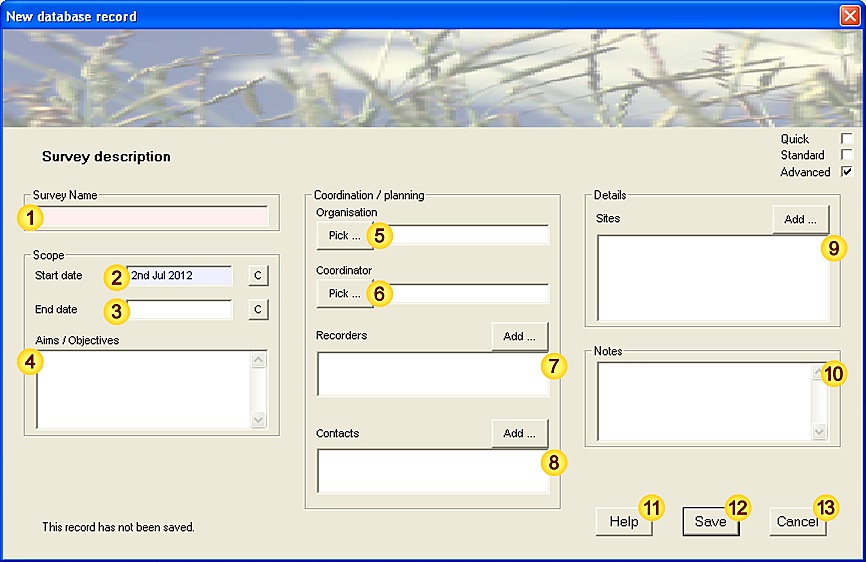
| Survey | The Survey that this Observation relates to (if any). [Fixed-length field - 80 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Sample ID | Any identifier associated with this observation, for example if a small sample is removed for subsequent identification. [Fixed-length field - 32 characters max.] |
|||||||||||||
| Temperature | Ambient temperature at the time of the Observation, if relevant. | |||||||||||||
| Cloud-cover | Cloud-cover at the time of the Observation, if relevant. [Values: 0 - 8 octas.] [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Wind-speed | Wind-speed at the time of the Observation (Beaufort scale) if relevant. [Values: '0 - Calm', '1 - Light air', '2 - Light Breeze', '3 - Gentle Breeze', '4 - Moderate Breeze', '5 - Fresh Breeze', '6 - Strong Breeze', '7 - Near Gale', '8 - Gale', '9 - Severe Gale', '10 - Storm', '11 - Violent Storm'.] [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Precipitation | Rain- or snowfall at the time of the Observation, if relevant. [Values: None, Mist / drizzle, Light rain, Heavy rain, Snow.] [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Card reference | Cross-reference with paper-based record. [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Photograph reference | Cross-reference to any accompanying photograph - may be an identifier, album (or other retrieval system) reference or file path. [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Fast filters | Field patterns (approx 65000 combinations) for fast data-grouping / filtering. | |||||||||||||
| Notes | Any additional notes (double-click to resize). [Free-text field - no maximum length.] |
|||||||||||||
| Help | View this help page. | |||||||||||||
| Save | Save data as new record. | |||||||||||||
| Cancel | Cancel the form. | |||||||||||||
3. Additional Notes.
3.1. Input Date and Time formats
Any date / time format that is not ambiguous is acceptable, with few restrictions on separators. For example:
| Acceptable Date / Time data formats | ||
|---|---|---|
| 3 Sep 2006 3-Sep-2006 3:Sep:2006 | Valid | Unambiguous |
| 3rd September 2006 | Valid | Unambiguous |
| 3 Sep 2006 2:10:00 | Valid | Unambiguous |
| 3/9/2006 | Invalid | Day/Month order is ambiguous [NB: 26/9/2006 is valid] |
| 3 Sep 06 | Invalid | Day/Year order is ambiguous [NB: 3rd Sep 06 is valid] |
 ), which form the higher levels of the classification tree,
), which form the higher levels of the classification tree, ), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
 ), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,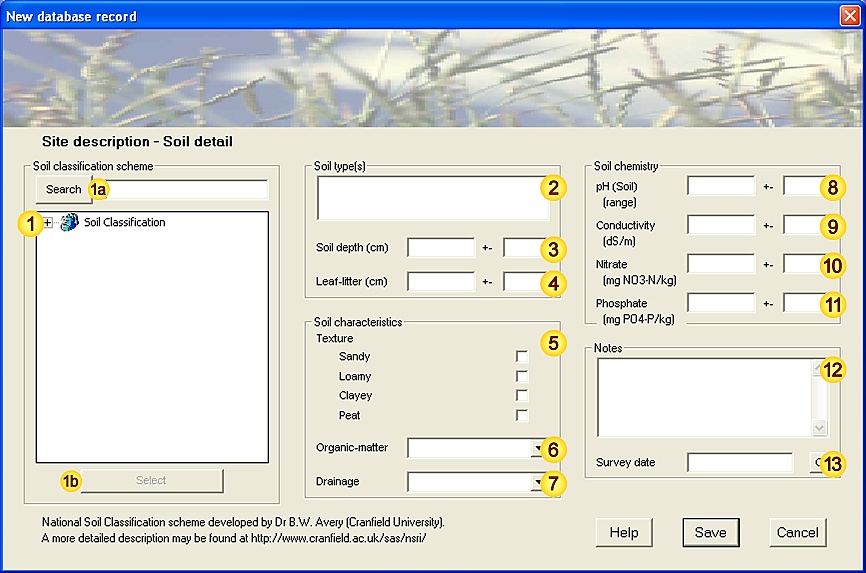
 ), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,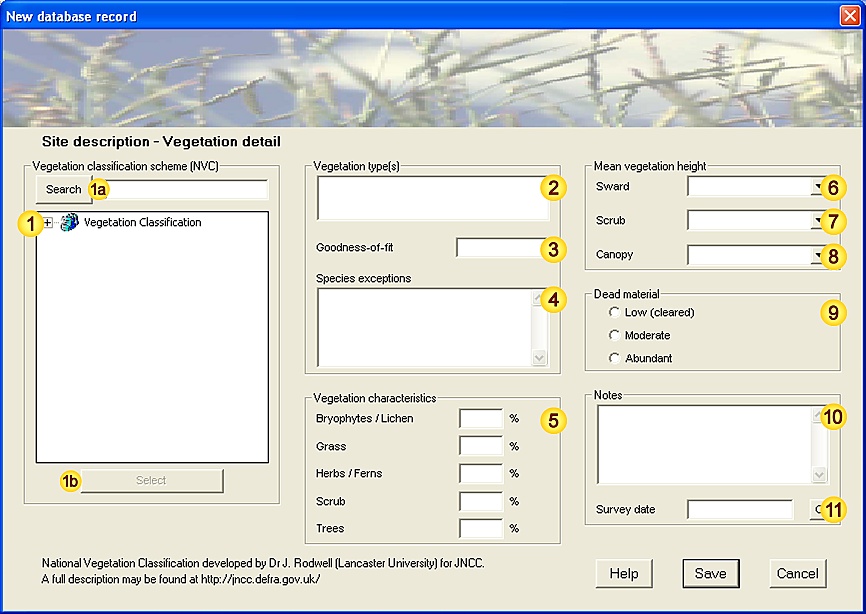
 ), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,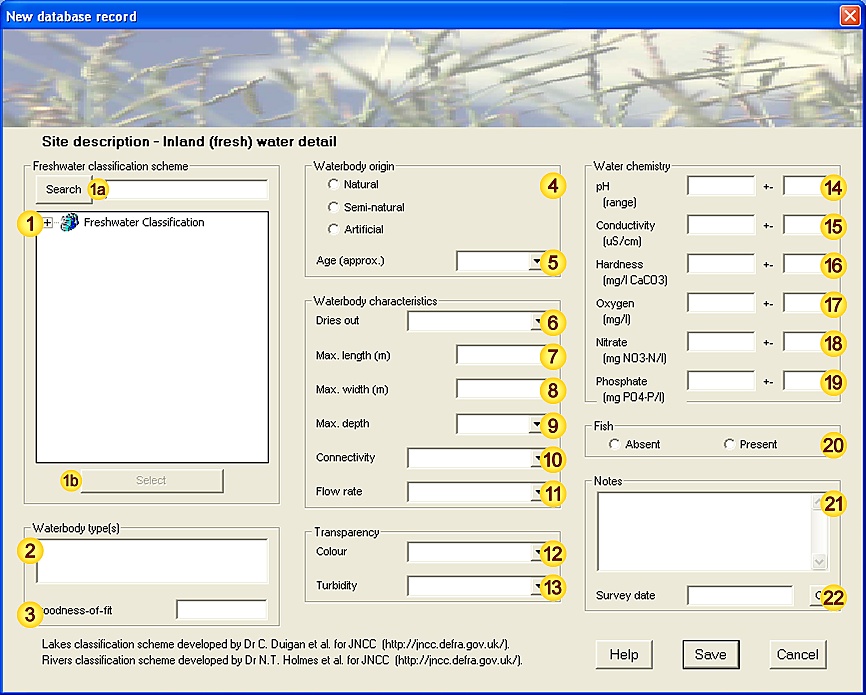
 ), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,
), which occupy the lowest levels of the classification tree,